In this article, we introduce you to the concept of monopolistic competition and how you can navigate if your brand is stuck in a monopolistic market.
From Apple v/s IBM v/s HP, Netflix v/s Blockbuster v/s Disney to Facebook v/s Snapchat v/s Twitter – business wars are an inevitable aspect of business building.
Many newbies try to head-on compete with an existing bigger shark in the market. Small businesses and newly launched startups find it difficult to compete in such a situation. But by knowing how a monopoly-like market works, you can strategize and navigate for better chances of success. Read further to know more about monopolistic competition.
What is monopolistic competition?
Monopolistic competition is a market situation where companies offer services with very little competitive differentiation.
It is one of the forms of the monopolistic market but it shouldn’t be confused with the others like pure competition. Companies involved in a Monopolistic competition do not necessarily substitute for each other.
However, none of the companies in a monopolistic competition structure enjoys a full monopoly.
It is common in a monopolistic competition structure for companies to innovate constantly. This is because of the need to stay ahead of their competitors and have a stronghold in the market. They also have big marketing budgets because it is another way to differentiate them in the monopolistic market. Below is a deep dive into what a monopolistic market is.
What does a monopolistic market look like?
Do not confuse Monopolistic competition with a monopolistic market.
In a monopolistic market a single company, often big, gets to control the market in terms of price, demand, and supply. This creates a high barrier to entry for new businesses and limited options for consumers.
Usually, innovations create a monopolistic market. For instance, an inventor who is the first to discover a technology will have a monopoly over it for a while due to patenting. Monopolies are bad for consumers, and eventually, the economy. It gives them the power to manipulate prices at their will. To avoid this, governments often step in with antitrust laws.
An example of a monopoly is Microsoft with windows and de beers group with diamond mining. Another classic example is John D Rockefeller's oil production company in 1870s America.
How is Monopolistic competition different from Perfect Competition and Monopoly?
Monopolistic competition, Perfect Competition, and Monopoly are controversial market structures that tend to cripple innovation. With too much pricing power in a few hands, one doesn’t take efforts to improve customer experience.
Let us understand the difference between them so that you are better able to navigate your business that falls in such markets:
Monopolistic Competition vs Perfect Competition
Perfect or pure competition is one where a level playing ground exists for companies selling similar products. This market structure has a low barrier to entry, and the price of goods is dictated by demand and supply. The customer too has multiple choices and transparent knowledge of products.
Here are some of the key differences between monopolistic competition and perfect competition.
-
Under perfect competition, businesses have products or services that are substitutes for each other. There is a slight difference between the output of competing businesses when there is monopolistic competition.
-
In monopolistic competition, the strong similarities between the products and services create a non-compete pricing structure. Hence, marketing activities such as promotion and advertising are prioritized for product differentiation. These marketing schemes emphasize the quality and uniqueness of products to win the buyer. Perfect competition does not require much differentiation. Prices are determined by whatever majority gets paid in the case of online shopping. Or it's controlled by authorities, for example, government-controlled vegetable markets.
-
The pricing power in monopolistic competition is skewed and easy to exploit. For instance, if a business wants to sell more, it will drastically reduce prices to put the competition out of business. This is exactly what Reliance Jio, a telecom giant in India, used as its go-to-market strategy. India’s telecom market was monopolistic with 2-4 key players. Jio released free SIM cards with unlimited data, prompting people to switch from other carriers. You cannot pull off such tactics in perfect competition.
-
Entry and exit in a perfect competition market are much easier than it is in a monopolistic competition.
-
Finally, most economists have argued that perfect competition is merely a fictitious market structure. That is, it doesn’t exist in the real world and it’s only speculation of what an ideal market structure should be. Monopolistic competition, on the other hand, exists in the real world and can be found in most countries.
Monopolistic Competition vs Monopoly
A monopoly is a market structure where one company enjoys a very large market share. This type of market structure is frustrating for customers as they don’t get choices. They have to bear with the monopoly’s product irrespective of quality or customer experience. It differs from the monopolistic competition as follows:
-
The stakeholders in monopolistic competition are often multiple, more than 5. In a monopoly, one business or company is enough for it to exist.
-
Compared to a Monopoly, Monopolistic Competition has a lower entry barrier. A monopoly company does all it can to kill competition by copying products or acquisitions, for example, Facebook.
-
Competition for the available markets is present in a monopolistic competition market structure. In a monopoly, however, there is no competition. For example, Google hardly has any competition in the digital search advertisement market.
-
Prices in a monopoly are controlled by a single company. Price in monopolistic competition is controlled by the demand-supply. But companies with deeper pockets in cash flow can manipulate the market for their benefit.
What are the monopolistic competition characteristics?
The following are the characteristics that make up a monopolistic competition market structure:
-
Very similar products
The products offered in a monopolistic competition don’t have many differences between them. For instance, instant noodle brands like Maggi, Yippee, etc are in a monopolistic competition market structure. There is barely any difference between packs of noodles and their ingredients, but some differences in taste do exist.
-
Free market
A monopolistic competition market is a very flexible one that businesses can enter and leave at will. Barring the cost required to start a business, the cost of entering and exiting is low.
-
Multiple companies
For monopolistic competition to exist, many companies have to be producing similar products and selling them to the same customers. They try to differentiate based on value propositions and marketing.
-
Profits
The businesses in monopolistic competition are profit-oriented. Different participants share profit and are not gobbled by a single business.
Monopolistic competition examples
Monopolistic competition exists in different industries and countries.
-
Fast food companies
Burger King, McDonald’s, and KFC are all in monopolistic competition in this industry
-
Retail stores:
Most franchise stores like Walmart, Target, and Costco are in a monopolistic competition.
-
Shoe-making companies:
Companies that make footwears often make similar products. Nike, Adidas, and Reebok all cater to the same market.
Strategies to beat monopolistic competition
Every entrepreneur wants their business to grow exponentially, sometimes, irrespective of market forces. It’s crucial to conduct a competitive landscape analysis before strategizing on the next steps. Here are some ways to beat a monopolistic competitive market:
Adopt aggressive marketing campaigns
The marketing budget of businesses in monopolistic competition is always big. They exist in a market structure where being unique is important – and promotion and advertisement are one way to achieve this. Businesses spend on their product packaging and branding to attract and retain customers.
Many businesses engage in dissing each other via advertisement wars, a classic example being McDonalds v/s Burger King.

Source: Mad Over Marketing
Enhance customer experience
A loyal customer helps with word-of-mouth – which further acts as a defensive moat. Amazon, among thousands of eCommerce platforms, has a sharp focus on customer experience. It has not only helped it compete with other stores but also turn eCommerce into a monopolistic market.
Enhance quality
Offering high-quality services and products builds a loyal customer base despite the competition. Being the best is easily one of the best ways to stand out. Netflix uses this strategy of catering to premium users in the rush of OTT platforms. Even with less subscriber base in India, Netflix enjoys similar revenues compared to Disney + Hotstar.
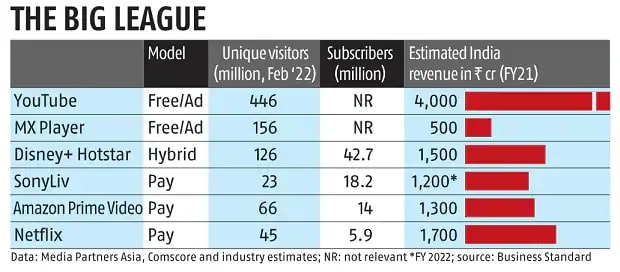
Source: Business Standard
Learn more about monopolistic market
While monopolistic competition is one of the most popular market structures, it is not the only one that exists. Businesses are advised to observe and understand them to increase their chances of scaling. You can learn more about monopolistic competition with the below resources:
-
Monopolistic Competition by David Harvey's Anti-Capitalist Chronicles
-
Game Theory and Oligopoly: Crash Course Economics #26
-
Making Sense of Our Very Competitive, Super Monopolistic Economy by Walter Frick
-
Episode 438: Mavericks, Monopolies, And Beer by Planet Money





 Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship